FOLIC ACID & FOLATE: Are they the same or different?
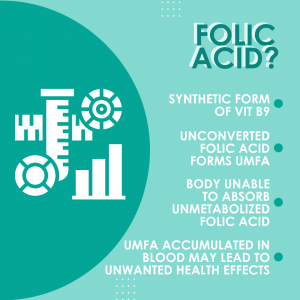

The terms folic acid and folate are constantly used interchangeably in the world of nutrition. In actual fact, these two elements are different forms of the same vitamin, Vitamin B9. Folic acid is the synthetic form (non-active form) whilst, folate is the natural occurring form of vitamin B9.
Functions of Vitamin B9:
Aid in the growth of various tissues and cells in the body.
Work synergistically with Vitamin B12 and Vitamin C to aid in the breakdown of protein and formation of new protein, making it readily available for use by the body.
Reduce or prevent folate deficiency anemia
Help produce DNA, the building block of the human body, which carries genetic information.
Produce healthy red blood cells which are critical during periods of rapid growth, such as during pregnancy and fetal development.
Prevent birth defects of the brain and spine known as neural tube defects (spina bifida)
Aid in reducing the buildup of homocysteine in the body.
In recent years, homocysteine has caught the attention of many researchers, as high levels of this amino acid can wreak havoc in the human body. From increasing risk of osteoporosis to heart disease to dementia. High homocysteine levels usually indicate a deficiency in Vitamin B-12 or folate.


Foods rich in folate:
- Dark green leafy vegetables (turnip greens, spinach, romaine lettuce, asparagus, Brussels sprouts, broccoli)
- Beans
- Peanuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Fresh fruits, fruit juices
- Whole grains
- Liver
- Seafood
- Eggs
- Fortified food items. (eg: cereals, breads, rice, pasta, and other grain products).
Apart from getting folate from food sources, it is also available in the form of supplements. Most of the supplements in the market currently contain folic acid compared to active folate (in the form of 5-MTHF). One of the advantages of supplements that contain active folate is that it is biologically active, making it more easily absorbed and utilized by the body.
The best way to optimize folate intake is to consume a well-balanced diet with all major food groups; carbohydrate, proteins, fats, vegetables, fruits, etc. However, our hectic lifestyles makes it tough to implement this at every meal.
Hence, it is encouraged to take a folic acid supplement daily, preferably one with active folate, to enhance folate stores in the body and reduce the risk of health complications.
lifstyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility lifestyle factors & fertility
TURBOPOWER FOR SPERM CELLS
Highly effective.
A spermiogram assesses the concentration, mobility and shape of sperm cells. The video on the right shows the distinct difference after 3 months of taking PROFORTIL®.
Male infertility has many causes – in industrialized countries, genetics, stress, changes in life patterns and dietary habits all lead to dramatic reductions in sperm cell production and quality. PROFORTIL® is a clinically-tested and patented formula, developed specifically to optimize sperm quality and to treat male sterility. Clinical studies show that taking PROFORTIL® for at least 3 months significantly improves sperm quality. No other formula has beaten its pregnancy rate of Ø 26-41%.
An important factor for a healthy baby
Breaks in sperm DNA strands greatly increase the chances of miscarriage
In the process of cell division, DNA is copied and transferred to each new cell. If the DNA strands in sperm are damaged, the process of cell division may be disrupted, stopping embryonic development entirely. PROFORTIL® reliably protects sperm DNA from damage.
During cell division, DNA is transferred to each new cell just like a train transfers cargo to a destination. If a train’s tracks are damaged, the train cannot make it to the destination. The same is true when DNA strands are damaged. Both the train and the DNA are derailed.
If there are serious breaks in the DNA (genetic information is “broken”, “damaged”), new cells will be incomplete and unable to continue the cell division process. Embryonic development stops.
Infertility is the medical term for sterility. This is the case when regular sexual intercourse without contraception does not lead to pregnancy within 12 months.
There is a general distinction between primary and secondary infertility:
Primary infertility:
The man has never fathered a child before.
Secondary infertility:
The man has already fathered one or more children, whether with his current partner or another woman.
In many cases of infertility, the woman is examined before the man; although in about half of all cases, the cause is found in the man.
Male infertility can have many causes. Genetics, stress, changes in life patterns and dietary habits all lead to a dramatic reduction in sperm cell production and quality. The wish to have a child is still denied to around 15% of all couples, even after one year of unprotected sexual intercourse.
A fundamental distinction is made between inherited and acquired disorders. Furthermore, a distinction is made between diseases relating to hormonal control of testicular function (approx. 12%), diseases of sperm formation in the testicles (approx. 30-40%) and diseases of the sperm transport system (approx. 10-20%).





