Why Women Get More UTIs Than Men -- and what they can do to stop it
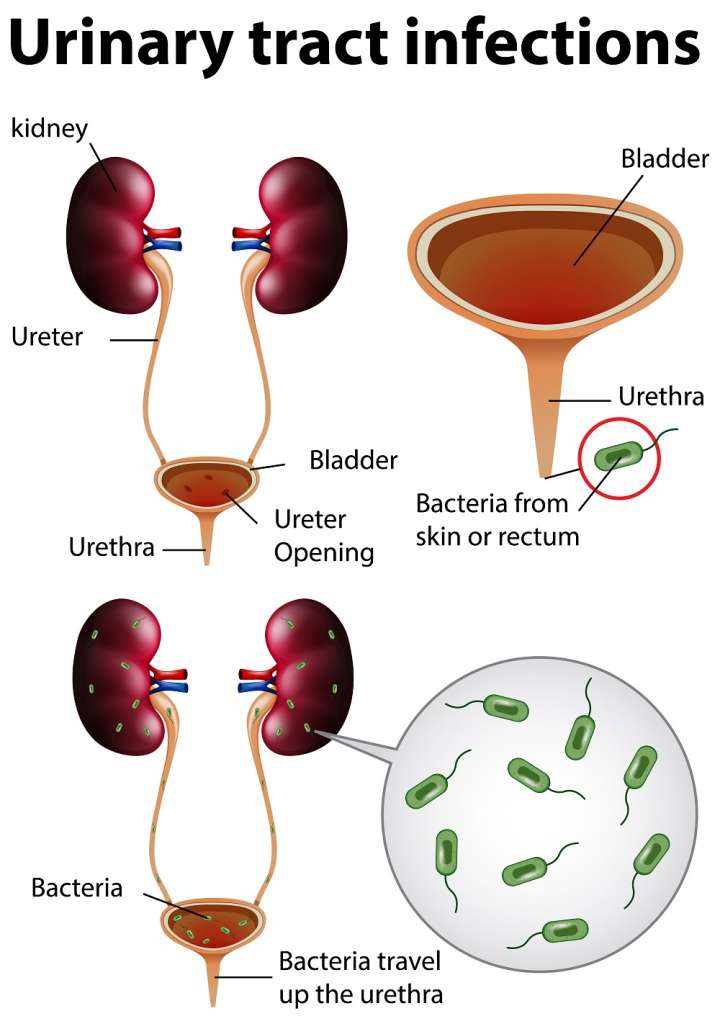
Here are some not-so-fun facts for you ladies out there: women get urinary tract infections (UTIs) as many as 30 times more often than men do. As if this statistic is not shocking enough, the US Department of Health and Human Services shared that 4 out of 10 women who get UTIs will get it again within a six month period.
You can thank your anatomy for this. A woman’s urethra (the tube from the bladder to where the urine comes out of the body) is shorter than a man’s, making it a whole lot easier for bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) to enter the bladder. You might want to remember this particular bacteria too — 51% of bladder infections (which leads to UTIs) are caused by E. coli.
However, that is only one of many reasons why women are more prone to UTIs than their male counterparts. Dr. Boyd Clary of Virginia Physicians for Women explained:
▪ Women have sensitive skin lining the inside of their vaginas. Because of this, the female urethra is much easier to traumatise and irritate, creating the perfect environment for bacteria to thrive and climb up towards the bladder.
▪ The urethra placement in women is just closer to the anus, the main source of waste and bacteria.
▪ Even sexual contact can allow bacteria to get near the vagina and eventually the bladder, so sexually active women are even more at risk when it comes to UTIs.
▪ Specific types of contraception like spermicide or a diaphragm can further increase recurrent UTIs.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) ?
But wait — what exactly is a UTI, and how do you know if you have it?
–> Chances are you might have already experienced such a thing and was prescribed antibiotics by your general practitioner.
Here are some symptoms you should look out for according to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention:
■ Pain or burning while urinating
■ Frequent urination
■ Feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder
■ Bloody urine
■ Pressure or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen
Less common but possible symptoms of a UTI:
■ Fever
■ Chills
■ Lower back pain or pain in the side of your back
■ Nausea or vomiting

Can You Stop It From Happening?



